Admin Setup Guide
Complete guide for administrators to create and configure semantic domains
Navigating to Domains
- Log in to Semaphor
- Select your project from the project list
- Click on "Domains" tab in the top navigation
Creating a Domain
Step 1: Create a New Domain
- On the Domains page, click the "Create Domain" button
- Fill in the domain details:
- Name: A unique identifier (e.g.,
sales_analytics) - Label: User-friendly display name (e.g.,
Sales Analytics) - Description: Brief explanation of what this domain covers
- Connection: Select the data connection this domain uses
- Name: A unique identifier (e.g.,
- Click "Create" to save your domain
Quick Setup Summary
Before diving into the details, here's the complete workflow at a glance:
- Create Domain → Name it and select a connection
- Add Datasets → Select tables, let AI generate labels (30-60s per dataset)
- Discover Relationships → Run AI discovery, accept suggestions (1-2 minutes)
- Save & Test → Save domain, test in a dashboard card
Total time: 5-10 minutes for a typical domain with 4-5 datasets
The AI does most of the work! Semaphor automatically generates field labels, descriptions, and discovers relationships between your datasets. Your main job is reviewing and accepting suggestions.
Now let's walk through each step in detail.
Step 2: Open the Domain Editor
After creating your domain, you'll be taken to the Domain Editor, which has four tabs:
- Datasets: Add and configure your data sources
- Relationships: Define how datasets connect
- Code Editor: View and edit the domain as YAML/JSON
- Preview: Test your domain configuration
Adding Datasets
After creating your domain, you'll add the datasets (tables) you want users to explore.
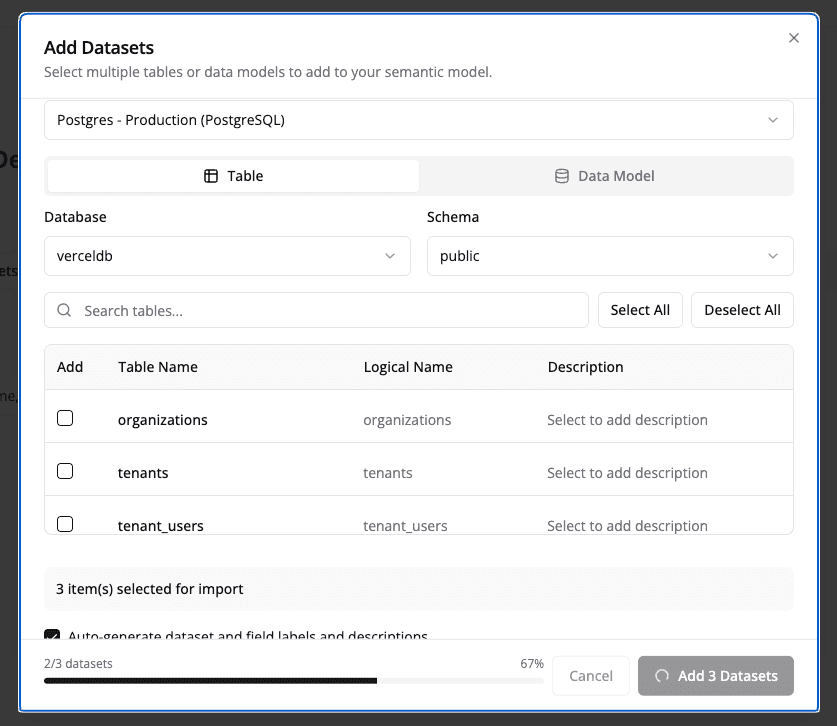
Step 1: Select Your Datasets
- In the Domain Editor, ensure you're on the Datasets tab
- Click the "Add Dataset" button
- Select the tables or views you want to include from your database
- Click "Add" to add each dataset
AI-Powered Labels: After adding datasets, Semaphor automatically generates user-friendly labels, field names, and descriptions using AI. This process takes a few moments but saves you from manually configuring each field.
Step 2: Wait for AI Processing
After you add datasets and click Save, Semaphor's AI automatically:
- Generates customer-facing labels for table names (e.g.,
orders_tbl→ "Orders") - Creates readable field names (e.g.,
cust_id→ "Customer ID") - Adds helpful descriptions for fields
- Classifies fields as dimensions (groupable) or measures (aggregatable)
- Suggests appropriate aggregation functions (SUM, COUNT, AVG)
Note: This AI operation typically takes 30-60 seconds per dataset. You'll see a loading indicator while processing.
Step 3: Review AI-Generated Fields (Optional)
After AI processing completes, you can review and adjust the generated labels:
- Click the "Edit" button (pencil icon) next to a dataset
- Review the AI-generated field labels and descriptions
- Make adjustments if needed (most users find the AI labels work well as-is)
- Hide any fields that shouldn't be visible to end users
Advanced: You can also create virtual datasets using custom SQL queries. See the Advanced Configuration section below.
That's all you need to get your datasets ready! The AI handles the labeling and classification automatically. Next, you'll define how these datasets relate to each other.
Creating Relationships
Relationships define how datasets connect to each other, enabling automatic joins when users explore data across multiple datasets.
Recommended Workflow: Use AI Discovery to automatically identify relationships. Most users find they don't need to manually define any relationships after using AI discovery.
Using AI-Powered Relationship Discovery
Semaphor can automatically discover potential relationships between your datasets using AI analysis of field names, data types, and semantic patterns. This is the fastest way to set up your domain.
The relationship discovery process typically takes 1-2 minutes to complete.
The entire process takes just a few steps:
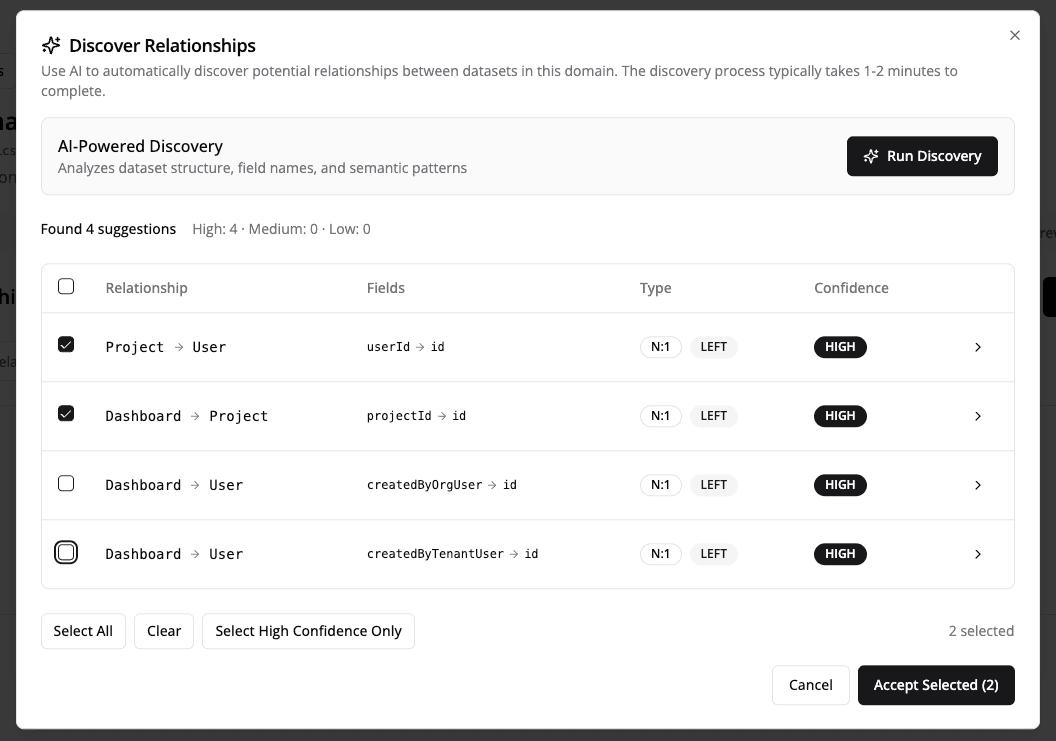
- Click "Discover Relationships" in the Relationships tab
- Click "Run Discovery" and wait 1-2 minutes while AI analyzes your datasets
- Review the suggestions - each shows confidence (High/Medium/Low) and rationale
- Select relationships to add - use "Select High Confidence Only" or review each one
- Click "Accept Selected" - done!
What the AI analyzes:
- Field names (e.g.,
customer_idlikely joins tocustomers.id) - Data types (matching types for join keys)
- Semantic patterns (fact tables to dimension tables)
- Table structures (primary/foreign key patterns)
What you'll see in suggestions:
- Source → Target: Which datasets connect (e.g.,
orders → customers) - Join Fields: Which fields match (e.g.,
orders.customer_id = customers.id) - Confidence: High, Medium, or Low
- Rationale: Why the AI thinks this relationship exists
- Cardinality: One-to-one, one-to-many, etc.
Tip: Start by accepting only High Confidence relationships. You can always run discovery again or manually add relationships later.
That's it! After accepting relationships, your domain is ready for users to query. The relationships enable automatic joins when users select fields from multiple datasets.
Advanced: Manual Relationship Management
Note: Most users don't need to manually create relationships after using AI Discovery. This section is for advanced use cases.
If you need to manually add or edit a relationship:
- In the Relationships tab, click "Add Relationship"
- Fill in the relationship details:
- Name: Identifier (e.g.,
orders_to_customers) - Source/Target Datasets: Which datasets to connect
- Join Fields: Which fields to match
- Cardinality: One-to-one, one-to-many, etc.
- Join Type: INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, or FULL
- Name: Identifier (e.g.,
- Enable Auto-Join to allow automatic join resolution
- Click "Save"
When to manually add relationships:
- AI didn't detect a relationship you know exists
- You need to specify a specific join type (e.g., INNER vs LEFT)
- You're working with non-standard naming conventions
- You need composite key relationships (multiple join fields)
Testing Your Domain
Step 1: Save Your Changes
After configuring datasets and relationships:
- Click the "Save" button in the top-right corner
- Wait for the confirmation message
- Your changes are now persisted
Step 2: Preview the Domain
- Click the "Preview" tab in the Domain Editor
- You'll see a summary of your domain:
- All datasets with their field counts
- All relationships with source/target info
- Validation warnings (if any)
Step 3: Test in a Dashboard
- Create a new dashboard or open an existing one
- Add a new card
- Select "Semantic Domain" as the data source
- Choose your domain from the dropdown
- Try selecting fields from different datasets
- If relationships are configured correctly, joins happen automatically
- If fields from unrelated datasets are selected, you'll see an error
Advanced Configuration
Advanced Dataset Configuration
Creating Virtual Datasets
Virtual datasets allow you to define custom SQL queries as reusable datasets. This is useful for:
- Pre-aggregated data (e.g., monthly revenue summaries)
- Complex transformations
- Combining multiple tables with custom logic
To create a virtual dataset:
- Click "Add Dataset" and select "Virtual Dataset"
- Enter a dataset name (e.g.,
monthly_revenue) - Write your SQL query:
- AI will generate field labels for your query results
- Click "Add Dataset"
Virtual datasets are materialized as subqueries when used in joins or filters.
Manual Field Configuration
If you need to manually adjust field properties beyond what AI generates:
- Click "Edit" on a dataset
- For each field, you can modify:
- Label: User-friendly display name
- Description: Help text explaining the field
- Data Type: String, Number, Date, DateTime, Boolean
- Field Type: Dimension (groupable) or Measure (aggregatable)
- Aggregate Function: SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX for measures
- Visibility: Show/hide from users (eye icon)
Best practices:
- Use clear labels: "Order Date" instead of "ord_dt"
- Add descriptions to help users understand fields
- Mark dimensions correctly for proper grouping
- Set default aggregations for measures
Domain Template Schema
Every semantic domain is stored as a template that defines datasets, relationships, and calculated fields. Understanding the schema helps with advanced configuration, version control, and CI/CD pipelines.
For a step-by-step tutorial on writing templates by hand, including how they translate into SQL queries, see the Template Guide.
Template Structure
Dataset Schema
Each dataset in the datasets array has this structure:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | string | Yes | Unique identifier for the dataset |
label | string | Yes | User-friendly display name |
description | string | No | Help text for users |
type | physical | virtual | Yes | Physical table/view or custom SQL |
connectionId | string | Yes | ID of the data connection |
connectionType | string | Yes | Database type (PostgreSQL, MySQL, etc.) |
schema | string | No | Database schema name |
table | string | No | Table name (for physical datasets) |
sql | string | No | Custom SQL query (for virtual datasets) |
fields | object | Yes | Field definitions (see below) |
primaryKey | string[] | No | Primary key columns |
Fields Object:
Relationship Schema
Each relationship in the relationships array:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | string | Yes | Unique identifier |
sourceDataset | string | Yes | Name of source dataset |
sourceFields | string[] | Yes | Join columns in source |
targetDataset | string | Yes | Name of target dataset |
targetFields | string[] | Yes | Join columns in target |
cardinality | enum | No | one_to_one, one_to_many, many_to_one, many_to_many |
defaultJoinType | enum | Yes | INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL |
isAutoJoin | boolean | Yes | Enable automatic join resolution |
discoveredBy | enum | Yes | user, auto, fk_constraint, ai |
isActive | boolean | Yes | Whether the relationship is active |
Calculated Metric Schema
Calculated metrics are stored in calculatedMetrics as a record (name → definition):
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
label | string | Yes | Display name |
description | string | No | Help text |
expression | string | Yes | Calculation formula with {input} tokens |
inputs | object | Yes | Input field references |
metricType | enum | No | base, derived, calculated |
format | object | No | Display formatting options |
tags | string[] | No | Categorization tags |
Calculated Dimension Schema
Calculated dimensions are stored in calculatedDimensions as a record:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
label | string | Yes | Display name |
description | string | No | Help text |
expression | string | Yes | SQL expression with {input} tokens |
inputs | object | Yes | Input field references |
dataType | enum | No | string, number, boolean, date, datetime |
Direct Template Editing
Power users can edit the domain template directly as YAML or JSON. This is useful for:
- Bulk edits: Rename multiple fields at once
- Version control: Store templates in Git for change tracking
- CI/CD pipelines: Automate domain updates as part of deployments
- Migration: Copy configurations between environments
For the complete field-by-field tutorial, see the Template Guide. For programmatic template generation (AI agents, scripts), see the Agent Guide.
Accessing the Code Editor
- Open your domain in the Domain Editor
- Click the Code Editor tab
- View and edit the full template as YAML or JSON
- Click Save to apply changes
Direct template edits bypass validation. Test thoroughly after making changes, especially to relationships and calculated fields.
Complete Template Example
Here's a full domain template for a sales analytics domain:
Domain-Level Calculated Fields
Add reusable calculated metrics and dimensions directly to your domain template. These fields become available to all users across all dashboards that use the domain.
Adding Calculated Metrics
Define metrics in the calculatedMetrics section of your template:
Adding Calculated Dimensions
Define dimensions in the calculatedDimensions section:
Best Practices for Domain Fields
- Document thoroughly: Include descriptions for every field. Users rely on this context.
- Use consistent naming: Follow a pattern like
metric_nameordimension_category. - Add tags: Group related fields (e.g.,
finance,marketing,operations). - Handle edge cases: Use
NULLIFfor division,COALESCEfor null values. - Test before publishing: Validate expressions with sample data.
Domain-level calculated fields appear in the Explorer with a Domain badge, distinguishing them from card-scoped or dashboard-scoped fields.
Next Steps
Once your semantic domain is configured:
- Train your users: Share the User Guide with end users
- Monitor usage: Track which relationships are used most frequently
- Gather feedback: Ask users which fields or relationships they need
- Optimize performance: Review query logs for slow multi-hop joins
- Expand gradually: Add new datasets and relationships based on user needs